
Compressor power formula : step by step explanations
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. Compressor power
simplified formula |
| 2. Explanation of
the formula : step by step |
1. Compressor power simplified formula
In MyEngineeringTools page dedicated to compressor power calculation, there are 2 formula given, a general formula, and a simplified one. The simplified one is the following, for 1 compressor stage of a perfect gas, the isentropic compression is :
Pis = 2.31*(k/(k-1))*(Tdis-Tsuct)/M*Qm
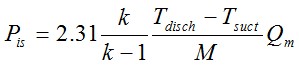
Equation 1 : simplified compression
power calculation formula
Top 5 Most
Popular
1. Compressor
Power Calculation
2. Pump Power Calculation
3. Pipe Pressure
Drop Calculation
4. Fluid Velocity in pipes
5. Churchill Correlation
(friction factor)
With : Pis=Power (kW)
Tsuct=Temperature inlet compressor (K)
Tdischarge=Temperature outlet compressor (K)
M=Molar weight of gas (g/mol)
Qm=Compressor throughput (t/h)
k=Gas isentropic coefficient
Now where this formula is coming from, where the 2.31 coefficient is coming from ? As we received a lot of questions on this matter, we decided to propose a dedicated page explaining how to reach this simplified expression, from the general one, as usual in a step by step approach which is the trade mark of MyEngineeringTools.com.
2. Explanation of the formula : step by step
STEP 1 : general equation
We need to start from a more general equation for isentropic compressor power calculation. According to [Perry], the adiabatic head of a compressor is given as :
Had = (k*Z*R*T1)/(k-1)*[(P2/P1)(k-1)/k-1]
With : Had= Adiabatic head (N.m/kg)
Z = gas compressibility factor (can be defined on an Amagat diagram
by calculating the reduced pressure and reduced temperature of the
gas)
P1 = Pressure inlet compressor (kPa)
P2 = Pressure outlet compressor (kPa)
k=Gas isentropic coefficient
R = 8314/molecular weight (J/(kg.K))
The work required during the compression is equal to the adiabatic head multiplied by the mass flow rate of gas, and divided by 1000 in order to express it in kW :
Pis (kW) = Had * Qm / 1000
With : Pis=Power (kW)
Had= Adiabatic head (N.m/kg)
Qm=Compressor throughput (kg/s)
1000 W/kW
This formula is also given on the other page [Perry] :
Pis = (k*Z*R*T1)/(k-1)*[(P2/P1)(k-1)/k-1]*Qm
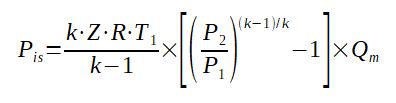
With : Pis=Power (W)
Z = gas compressibility factor (can be defined on an Amagat diagram
by calculating the reduced pressure and reduced temperature of the
gas)
P1 = Pressure inlet compressor (kPa)
P2 = Pressure outlet compressor (kPa)
Qm=Compressor throughput (kg/s)
k=Gas isentropic coefficient
R = [8314/molecular weight (J/(kg.K))]/1000 =
8.314/molecular weight
STEP 2 : Assumptions and simplifications
The general expression is using the gas compressibility factor Z, however in the simplified version we assumed that the gas is a perfect gas, as a consequence the factor is assumed to be 1 : Z = 1
R is actually equal to 8.314 (J/K/kmol) / M (kg/kmol) (see above), it can thus be replaced in the formula :

STEP 3 : Introducing isentropic compression
It is possible, via isentropic compression, to relate the pressure change to the temperature change :
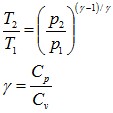
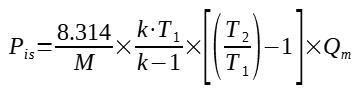
It can then be rearranged :
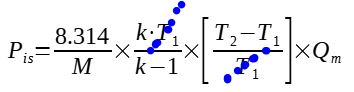
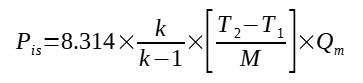
STEP 4 : Convert mass flow to t/h
The simplified formula is based on t/h while the general formula is considering kg/s.
We can then convert :
Qm_kgs / 1000 * 3600 = Qm_th
Qm_kgs = Qm_th * 1000 / 3600

Then 8314 / 3600 = 2.31, gives :
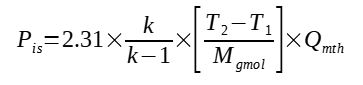
[Perry] Perry's Chemical Engineer's Handbook, Section 10 Transport and storage of fluids, page 10-45, McGraw-Hill, 2008