
Steam turbines : steam mass flow requirement calculation step
by step
Mass Flow of steam required to deliver a given power on a steam turbine
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
| Section summary |
|---|
| Introduction to
steam turbines |
| 1. STEP 1 : Define
the steam conditions |
| 2. STEP 2 : Get the steam thermodynamic
data at defined conditions |
| 3. STEP 3 : Calculate the enthalpy difference in between inlet and outlet conditions |
| 4. STEP 4 : Estimate the steam turbine
efficiency |
| 5. STEP 5 : Calculate the steam mass flow requirements |
| 6. Steam turbine steam mass flow requirement calculator |
Steam turbines are very common in process industries, especially large plants such as refineries or petrochemicals plants. This page is giving a calculation method to determine the flow of steam required to a steam turbine to produce a given power.
Introduction to steam turbines
A steam turbine is a device that converts the energy from pressurized steam into mechanical energy, which can then be used to generate electricity or perform other types of work.
Steam turbines are commonly used in power plants, where they are used to drive generators that produce electricity. They can also be used in marine propulsion and in large processing plants such as refineries where they will drive another machine, such as a compressor.
The steam is produced by heating water using a variety of fuel sources, including coal, natural gas, and nuclear energy in the case of a power plant. The pressurized steam is then directed through the blades of the turbine, which causes the blades to rotate and generate mechanical energy. This mechanical energy can then be used to power other types of machinery or generate electricity.
Steam turbines are highly efficient and reliable, and they are widely used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications. However, as they are rotating at very high speed, they require a very precise manufacture of the blades, balancing and maintenance.
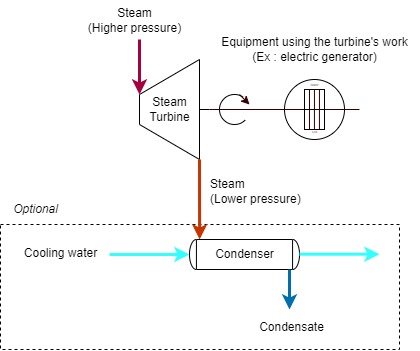
1. STEP 1 : Define the steam conditions
The Engineer must 1st determine which are the steam conditions at the inlet and outlet of the steam turbine that will be applied. For example, the inlet conditions may be known because there is a source of steam in the factory to be used, from a furnace or boiler for instance. The outlet pressure can be defined because of a specific requirement in the factory to use the steam downstream for other purposes.
For each condition, inlet and outlet, the pressure and the temperature of the steam must be determined.
P1 = pressure at inlet of the steam turbine (bar abs)
T1 = temperature at inlet of the steam turbine (c)
P2 = pressure at outlet of the steam turbine (bar abs)
2. STEP 2 : Get the steam thermodynamic data at defined conditions
For this step, it is necessary to have at hands steam tables, or a steam Mollier diagram.
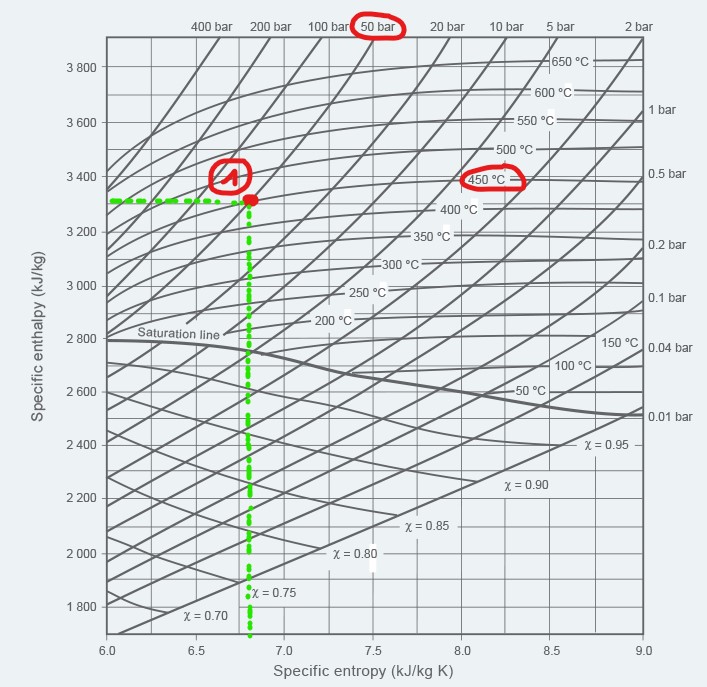
STEP 2.1 : At inlet conditions
The conditions at inlet, P1 and T1 are known. It is then possible to plot the conditions on the Mollier diagram and then calculate the specific entropy and the specific enthalpy of the steam.
Example :
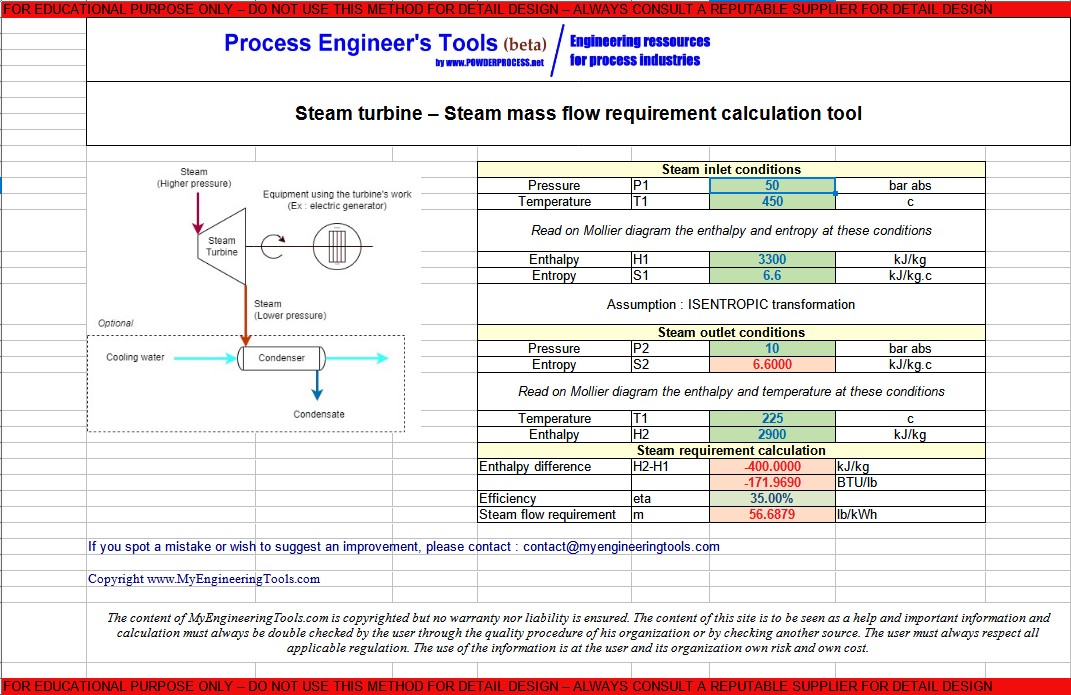
P1 = 50 bar abs
T1 = 450 c
The operating point of the steam in conditions 1 is represented on the Mollier diagram below. It is then possible to calculate :
H1 = 3300 kJ/kg
S1 = 6.6 kJ/kg.K
STEP 2.2 : At outlet conditions
Only the pressure P2 is known, it is necessary to determine the temperature as well as the enthalpy of the steam in the outlet condition, which is necessary to calculate the steam requirements of the turbine.
In order to determine these conditions, an assumption must be made on the transformation that the steam is submitted to in the turbine : it is isentropic. This means that entropy at inlet = entropy at outlet.
An isentropic transformation can be represented in the Mollier diagram by moving from condition 1 (inlet) to condition 2 (outlet) through a line of constant entropy. In the Mollier diagram used here, it means moving vertically accross the diagram until reaching the outlet pressure P2.
Example :
P2 = 10 bar abs
The operating point of the steam in conditions 2 is represented on the Mollier diagram below. It is then possible to calculate :
T2 = 225cH2 = 2900 kJ/kg
S2 = 6.6 kJ/kg.K (same as S1, isentropic transformation)
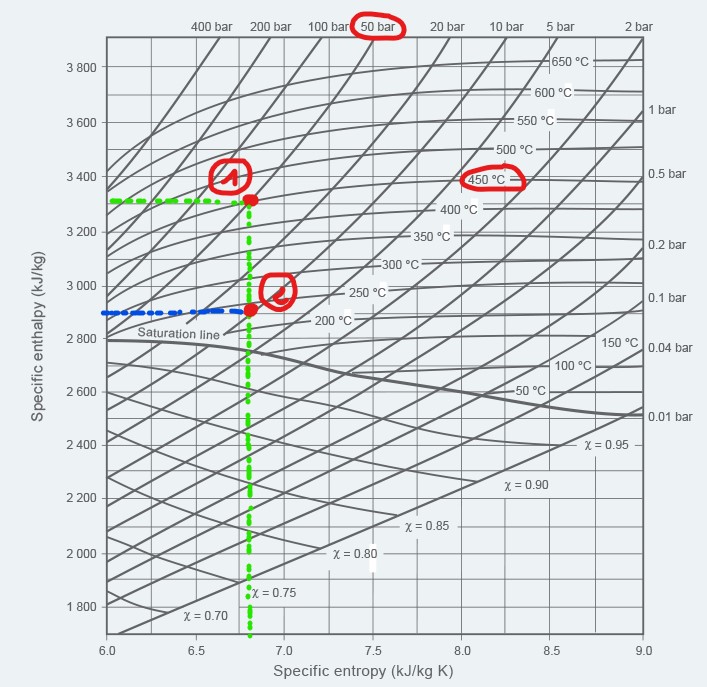
It is also worth to note that the outlet conditions remain above the saturation line. It means that the steam did not condense during its expansion.
3. STEP 3 : Calculate the enthalpy difference in between inlet and outlet conditions
The enthalpy has been calculated for conditions 1 and 2, giving H1 and H2. It is then possible to calculate the enthalpy difference of the steam when going through the turbine : ΔHs = H2 - H1
Example
H1 = 3300 kJ/kg
H2 = 2900 kJ/kg
ΔHs = H2 - H1 = -400 kJ/kg
For further purposes, this is converted to Btu/lb : -172 BTU/lb
4. STEP 4 : Estimate the steam turbine efficiency
It is necessary to know the turbine efficiency in order to calculate the steam requirements of a turbine. Indeed, not all the energy stored in the steam can be recovered by the turbine, there are losses that need to be accounted for in the steam turbine efficiency η.
Example
Considering that the steam turbine is non condensing, and assuming it is one stage, the efficiency would be 30-35%.
η = 35%
5. STEP 5 : Calculate the steam mass flow requirements
The steam requirement of a turbine can be estimated thanks to [Couper] :
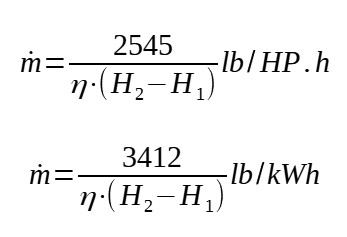
Depending on the power the Engineer wants to recover, the steam requirement in lb/h can be calculated.
Example :
ΔHs = H2 - H1 has been calculated and is equal to -172 BTU/lb
Then m = -3412/(0.35*(-172)) = 56.7 lb/kW.h
If the power expected is for example 50 kW, then the steam requirement will be : 5000 (kW) * 56.7 lb/kW.h = 2835 lb/h.
6. Steam turbine steam mass flow requirement calculator
The steam mass flow requirement for a steam turbine can be calculated thanks to this Excel steam turbine steam mass flow calculator : calculator
Warning : this calculator is provided to illustrate the concepts mentioned in this webpage, it is not intended for detail design. It is not a commercial product, no guarantee is given on the results. Please consult a reputable designer for all detail design you may need.
[Couper] Chemical Process Equipment Selection and Design, Couper et al, Gulf, 2005, page 63