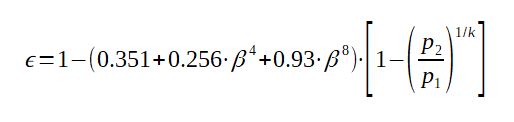Orifice plate (diaphragm) flow and pressure drop calculation
Definition, calculation formula and Excel calculator
Question or remark ? Please contact us at contact@myengineeringtools.com
1. Introduction
2. Pressure drop through an orifice
1. Introduction
Orifices are often used in fluid mechanics to limit mechanically the flow. The fluid going through an orifice plate will experience a pressure drop, it is therefore important to be able to size orifice plate correctly to adjust the flow as needed.
Note that measuring the pressure drop
through an orifice can also be used to measure the flowrate of the
fluid.
The restriction orifice mentioned here is a thin perforated plate, also called orifice plate or diaphragm.
2. Pressure drop through an orifice
How to calculate the pressure drop through an orifice plate ?
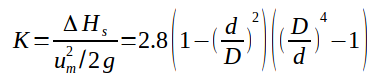
K = Pressure drop coefficient
D = Pipe diameter (m)
d = orifice diameter (m)
um = fluid velocity, before diaphragm, (m/s)
ΔHs = Pressure drop in m
The coefficient K can also be calculated thanks to the following graph :
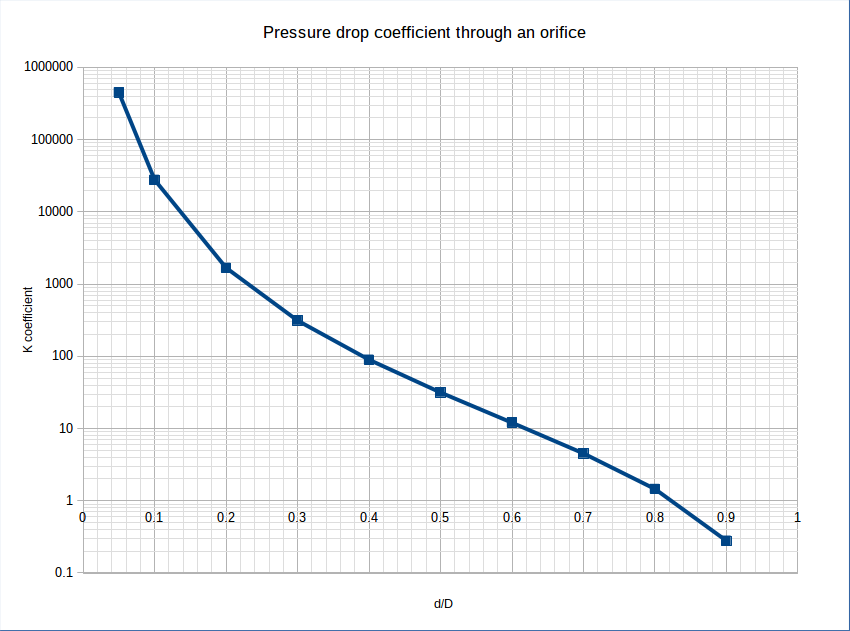
ISO 5167 is giving a more direct relationship that is used in the Calculator below.
qm=C/(1-β4)0.5*ε*π/4*d2*(2*ρ*ΔP)0.5
With :
qm = flow rate of the fluid through the orifice (kg/s)
C = coefficient of discharge (often 0.65 for an orifice plate)
β = d/D
ε = expansibility factor (for gas only, for liquid epsilon = 1)
D = pipe diameter (m)
d = orifice diameter (m)
ρ = fluid density upstream the orifice plate (kg/m3)
ΔP = pressure drop through the orifice plate (Pa)
The expansibility factor, for gases, can be calculated thanks to the following formula :
With :
ε = expansibility factor (for gas only, for liquid epsilon = 1)
β = d/D
p1 = upstream pressure (Pa)
p2 = downstream pressure (Pa)
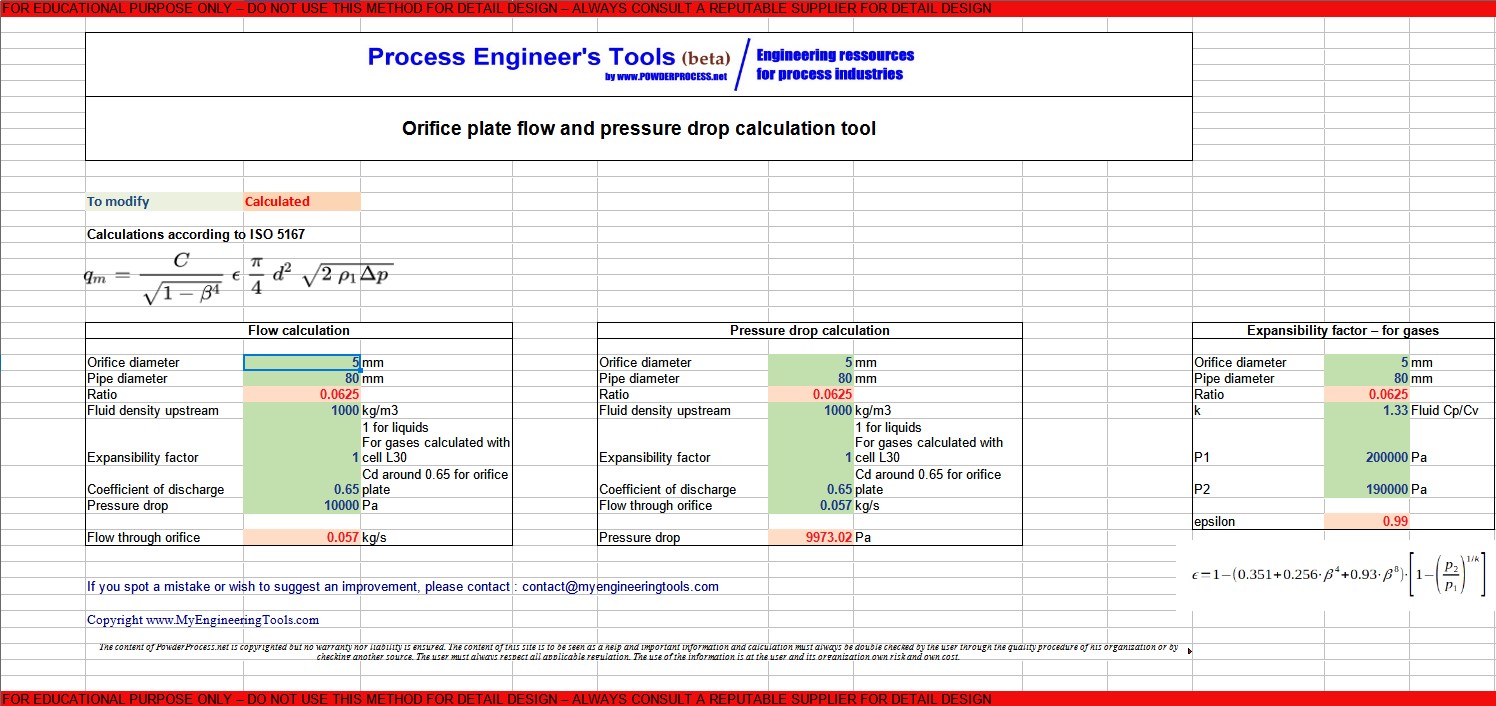
3. Orifice flow and pressure drop calculation tool
How to calculate the flow through an orifice plate ?
You can access to an Excel calculation tool in order to assess the
flow and pressure drop through an orifice plate : orifice
plate Excel calculation tool (click here)
Warning : this calculator is provided to illustrate the concepts mentioned in this webpage, it is not intended for detail design. It is not a commercial product, no guarantee is given on the results. Please consult a reputable designer for all detail design you may need.